The aging test mainly refers to the thermal oxygen aging test of rubber, plastic products, electrical insulation materials, and other materials; or the ventilation aging test for electronic parts and plastic products.
Seven aging test methods:
At present, there are many aging test methods for polymer materials, including climate aging test, ultraviolet aging test, ozone aging test, hot air aging test, high and low temperature alternating aging test, damp heat aging test, medium aging test, salt spray aging test, etc..
Climate Aging Test
The so-called climate aging test is a kind of research method that exposes the test samples of polymer materials to atmospheric environmental conditions, so as to obtain the aging law of the material samples exposed to the atmospheric environment, analyze the properties of polymer materials, and predict their service life.
There are two types of climate aging tests
- One of them is the natural exposure test, the polymer material test sample is exposed to the real atmospheric environment to obtain the aging behavior of the material in the real environment. The aging information obtained by this aging test method is the most accurate. The most effective method for the aging behavior of molecular materials, but this test method cycle time is too long, time-consuming, and laborious. People in Florida in the United States, Wanning, Mohe, and Wuhan in China have conducted air exposure tests for more than a year.
- The other is the artificial climate aging test. The artificial climate aging test refers to the aging test method in which people simulate the real atmospheric environmental conditions indoors or strengthen a certain environmental factor to obtain the aging behavior of materials in a short time. It is also called artificial simulated aging or artificially accelerated aging. Artificial climate aging is usually carried out in an artificial climate aging chamber. The commonly used artificial climate aging chambers mainly include xenon lamp climate aging chamber, fluorescent lamp climate aging test chamber, and carbon arc lamp climate aging test chamber. These types of climate aging test chambers simulate or strengthen natural environmental factors from the main climatic factors such as light, temperature, humidity, rain, or condensation to achieve material aging. In addition, the aging test materials should be carried out according to certain test standards.
UV Aging Test
Ultraviolet light in sunlight, because its light energy is equivalent to the bond energy of polymer chemical bonds, can cause the break of the polymer compound chain, which is the main factor leading to the degradation of polymer materials.
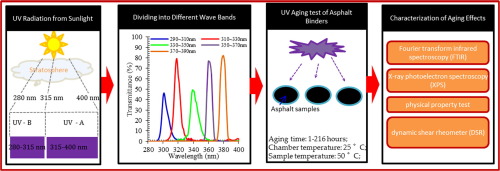
The ultraviolet aging test refers to a test method in which the aging test samples of polymer materials are placed in an ultraviolet light field and exposed to obtain the aging behavior and laws of polymer materials.
Generally, the ultraviolet aging test will specify the ultraviolet region and the radiation intensity, such as 40W/m2, in the wavelength range of 300nm-400nm. The light sources used in the UV aging test usually include xenon lamps, fluorescent lamps, tritium lamps, and deuterium lamps. Among them, xenon lamps can simulate the solar spectrum well, and fluorescent lamps can simulate the ultraviolet spectrum of sunlight well. The tritium lamp can provide strong energy, which is generally used for accelerated aging tests.
Ozone Aging Test
Ozone is an extremely rare gas in the atmosphere, but it is extremely destructive to polymer materials. Ozone can have an irreversible chemical reaction with unsaturated bonds and reducing groups in the chemical structure of polymer materials, resulting in oxidative degradation of polymer materials, thus losing the use-value. Especially for rubber materials containing double bonds, it exhibits extremely strong destructive power.
Ozone has strong activity. It can decompose more active atomic oxygen and chemically react with the double bonds in the rubber molecule, causing rubber aging, crack, and become brittle.
The ozone aging test of polymer materials is usually carried out in an ozone aging test chamber. The ozone is provided by an ozone generator and its concentration can be adjusted by mixing with air with a mixer. The concentration of ozone is generally determined according to the environmental conditions in which the material is actually used.
In addition, the temperature, humidity, and other factors in the ozone aging chamber can also be adjusted to achieve the purpose of the test, and obtain the ozone aging resistance of the material and the behavior and law of ozone aging.

Hot Air Aging Test
Heat is one of the main factors that cause the aging of polymer materials. Heat can accelerate the movement of polymer chains, cause polymer chains to break, generate active free radicals, and cause free radical chain reactions to cause polymer degradation or exchange.
The hot air aging test is one of the main test methods for evaluating polymer materials and studying the aging resistance of polymer materials. It is usually carried out in a constant temperature blast drying test chamber.
The temperature in the drying oven can be set according to the test requirements. The polymer materials are regularly sampled and tested when exposed to dryness to obtain the aging behavior and laws of the polymer materials, so as to modify the polymer materials in a targeted manner and improve their performance.

Temperature Alternating Aging Test
Temperature is another important factor leading to the aging of polymer materials. For polymer adhesives, high temperature can accelerate the movement rate of the polymer adhesive chain, and low temperature can cause internal stress in the polymer adhesive. Alternation leads to chain scission of polymer adhesives and degradation and aging.
For rubber, high temperatures can accelerate the thermal movement of the molecular chain and Crosslink the rubber. Low temperature can cause the rubber molecular chain to freeze, making it brittle, decreasing its elasticity, and aging.
High and low temperature alternating aging test is an aging test method to evaluate the temperature resistance of polymer materials. It is usually carried out in a temperature alternating aging test chamber, from a certain temperature T1 (generally room temperature) to a certain temperature at a constant heating rate T2, maintain the temperature of T2 for a certain period of time, then reduce the temperature to a certain temperature T3 at a constant cooling rate, maintain the temperature of T3 for a certain period of time, and then increase to T1, which is a temperature cycle. The cycle length can be determined according to specific test requirements.
Damp Heat Aging Test
Damp heat aging test is an effective method to evaluate the aging resistance of polymer materials under high humidity and high temperature environment. In a high-humidity environment, water can penetrate into the polymer material, causing the polymer material to swell, and some of the hydrophilic groups are hydrolyzed, leading to aging and degradation of the polymer material.
In addition, the penetration of moisture into the polymer material can also cause the dissolution and migration of additives inside the polymer material, such as plasticizers, compounding agents, and other substances, and affect the mechanical properties of the polymer material.
Under the action of high heat, heat can promote the infiltration of water. Heat promotes the intensification of the movement of polymer chains, reduces the intermolecular force, promotes the infiltration of water, and accelerates the degradation of polymer materials.
Different polymer materials have different formulas, so their damp-heat aging mechanisms are also different. When the damp-heat aging test is carried out, different aging standards should be selected according to different polymer materials.
The damp heat aging test is usually carried out in the damp heat aging test chamber, and the temperature and humidity can be set according to the test requirements.
Medium Aging Test
Certain polymer materials need to be immersed in a certain medium for a long time during use. For example, polymer materials on equipment that have been engaged in marine operations or submarine operations for a long time must be immersed in seawater for a long time, and certain parts of aviation aircraft must be exposed to aviation for a long time. All these require that the high molecular materials have strong dielectric aging resistance.
The media aging test is a commonly used test method for evaluating the media aging resistance of polymer materials and predicting their life in a certain medium. The medium used in the aging test can be prepared according to the specific environment in which the polymer material is used. It can be artificial seawater, saltwater, rainwater, acid-base solutions, fuel oil, and other organic solvents.
References:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0950061819314503
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/earth-and-planetary-sciences/organic-carbon
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/aging-temperature


